Psychosocial Recent Trends
In recent years, the attention on mental health in the workplace and community has increased substantially. Greater levels of attention is a positive step to improving a very challenging and often stigmatised topic. The Health and Safety Index benchmark results 2020 vs 2021, reported improvements in responses to “I feel comfortable talking about mental health” ↑ up 5%. This was the greatest positive improvement of all 55 benchmark questions.
Despite this improvement, the actual Health and Safety Index benchmark results for “feeling comfortable talking about mental health” are in the bottom quartile, indicating we have a long way to improve compared to other health and safety behaviours, conditions and practices.
We have also seen the introduction of several international and domestic guidance materials from regulators to assist with managing psychosocial factors in the workplace, e.g.
- ISO 45003: International standard for managing psychosocial risk at work
- SafeWork NSW: Code of Practice for Managing psychosocial hazards at work
- Western Australia Department of Mines: Code of Practice: Psychosocial hazards in the workplace
- WorkSafe Victoria: Proposed OHS Amendment (Psychological Health) Regulations
- SafeWork Australia: Model Code of Practice on managing psychosocial hazards at work (Code of Practice).
This article specifically provides a comparison between:
- ISO 45003: Occupational health and safety management – Psychological health and safety at work – gives guidance on managing psychological health and safety risks; and
- SafeWork Australia: Model Code of Practice: Managing psychosocial hazards at work.
For a detailed comparison, press the download button to receive a copy of our Psychosocial Hazard Factsheet: ISO 45003 vs Code of Practice.
Standards vs Code of Practice
In general terms, Codes of Practice provide detailed information on how you can achieve the standards required under Work Health and Safety (WHS) laws. Codes of Practice do not replace the WHS laws, but can be help provide an understanding on how to apply legal requirements.
Worth noting, Victoria will be the first jurisdiction in Australia to legislate the specific requirement for psychosocial risk assessments.
Similarities: ISO 45003 and Model Code of Practice
There are many common areas between ISO 45003 and the Code of Practice. Both documents address psychological health sources of harm and potential risk factors covering both job demands and job resources. Both of these documents provide guidance on the management of psychosocial workplace factors in relation to:
- Design or management of work
- Process and system
- Working environment
- Plant and equipment
- Interactions, cultures, values and behaviours.
Interestingly, both documents are very limited in their guidance on worker impacts and outcomes.
Differences: ISO 45003 vs Model Code of Practice
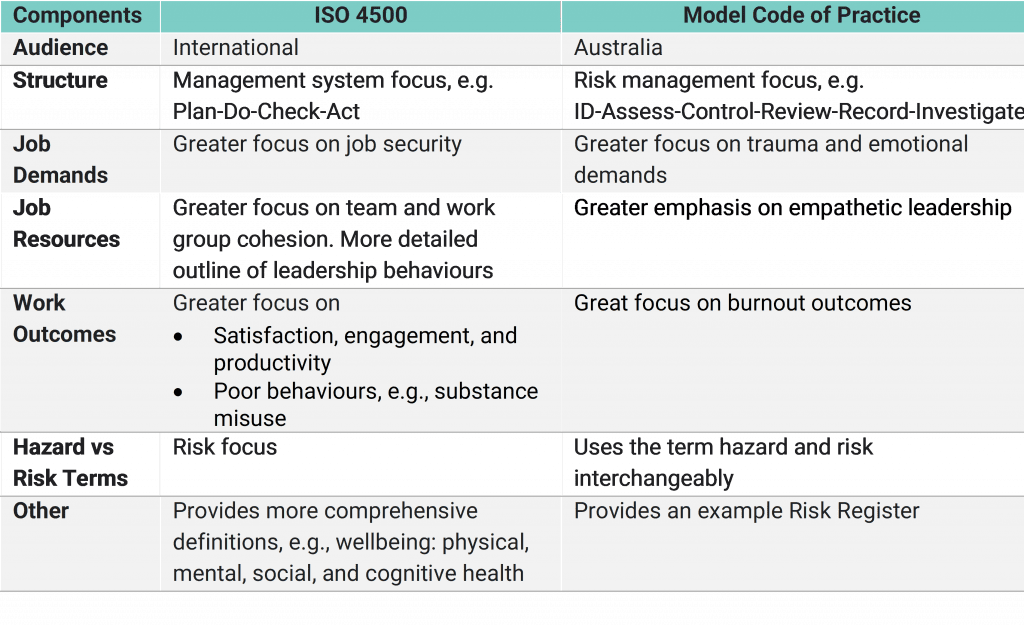
Despite ISO 45003 being 50% smaller by page number compared to the Code of Practice, it really provides a detailed outline managing psychosocial risks. Key distinctions with ISO 45003, are as follows:
ISO 45003
One of the most obvious differences between ISO 45003 and the Code of Practice is the structure of the guidance. ISO 45003 provides broader considerations to enable alignment with ISO 45001 OHS management systems (Plan-Do-Check-Act). This guidance is great for organisations with mature systems who can simply integrate the management of psychosocial factors into existing systems and practices. For more information on the relationship with ISO 45001, refer to our ISO 45003 vs 45001 blog.
ISO 45003 provides a greater guidance on the following areas:
- Job Demands: Greater focus on job security, uncertainty regarding work availability, non-standard employment that is low paid and/or insecure and working in situations that are not covered or protected by traditional employment laws or social protections.
- Job Resources: Greater focus on team and work group cohesion. It also provides a more detailed outline of leadership behaviours and activities Leaders can undertake.
- Worker Outcomes: Satisfaction, engagement, and productivity, poor behaviours, e.g., substance misuse
- Definitions: Provides more comprehensive definitions, e.g., wellbeing, physical, mental, social, and cognitive health.
Model Code of Practice
Compared to ISO 45003, the Code of Practice is structured to align with operational risk management principles (ID-Assess-Control-Review-Record-Investigate). Other key differences are the emphasis on trauma, emotional demands, and empathetic leadership. Although trauma is often associated with acute events, it also can be chronic or cumulative, e.g., “compassion fatigue” and repeated exposures to emotional situations. Compared to ISO 45003, the Code of Practice has a greater focus on the following areas:
- Structure: Aligned with risk management principles of hazard identification, risk assessment, risk control Review-Record-Investigations
- Job Demands: Greater focus on trauma and emotional demands
- Job Resources: Greater focus on empathetic leadership
- Appendix: Provides an example Risk Register.
Summary: ISO 45003 vs Model Code of Practice
A summary of key differences between ISO 45003 vs Code of Practice are outlined in Table 1 below
For a more detailed comparison, press the download button to receive a copy of our Psychosocial Hazard Factsheet: ISO 45003 vs Code of Practice.
So how can you use this information?

FEFO Consulting has partnered with the Health and Safety Index to design integrated online assessments to measure health AND safety performance supported by reliable benchmarks.
If you need help with Health and Safety, Wellbeing or Psychosocial maturity assessments, risk assessments, strategy, training, or other specific interventions – contact us today via email or call +61 1300 909 649
Subscribe: Click here





